Human DARS Protein (His Tag)
aspRS,HBSL
- 100ug (NPP2069) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P14278-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | aspRS,HBSL |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human DARS consists of 516 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 59 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 47 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 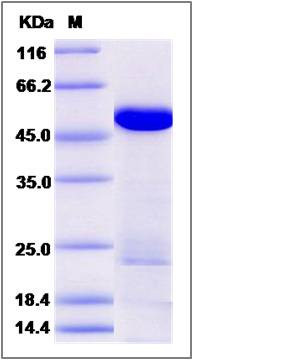 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human DARS (P14868) (Met1-Pro501) was expressed with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Epigenetics |DNA / RNA |Translation |tRNA synthetase |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM Nacl, 10% glycerol, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Aspartate tRNA ligase 1, also known as DARS, is part of a multienzyme complex of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. It belongs to the class-II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase family. DARS charges its cognate tRNA with aspartate during protein biosynthesis. DARS catalyzes the specific attachment of an amino acid to its cognate tRNA in a 2 step reaction: the amino acid(AA) is first activated by ATP to form AA-AMP and then transferred to the acceptor end of the tRNA. |
| Reference |
