Human DCAMKL1 / DCLK1 Protein
CL1,CLICK1,DCAMKL1,DCDC3A,DCLK
- 100ug (NPP2072) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11588-HNCB |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | CL1,CLICK1,DCAMKL1,DCDC3A,DCLK |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human DCLK1 consists of 707 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 78.5 KDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 64 KDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gly |
| SDS-PAGE | 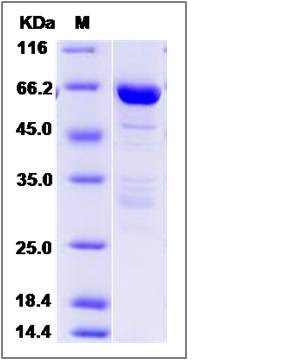 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human DCLK1 ( O15075-1) (Met 1-Val 705) was expressed and purified with two additional amino acids (Gly & Pro ) at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Kinase activity untested |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Protein Kinase |Intracellular Kinase |Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase (CaM Kinase) |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | DCAMKL1, also known as DCLK1, is a member of the protein kinase superfamily and the doublecortin family. It contains two N-terminal doublecortin domains, which bind microtubules and regulate microtubule polymerization, a C-terminal serine/threonine protein kinase domain, which shows substantial homology to Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase, and a serine/proline-rich domain in between the doublecortin and the protein kinase domains, which mediates multiple protein-protein interactions. DCAMKL1 is involved in several different cellular processes, including neuronal migration, retrograde transport, neuronal apoptosis and neurogenesis. Its microtubule-polymerizing activity is independent of its protein kinase activity. DCAMKL1 may be involved in a calcium-signaling pathway controlling neuronal migration in the developing brain. It may also participate in functions of the mature nervous system. |
| Reference |
