Human DNMT2 / TRDMT1 Protein (GST Tag)
DMNT2,DNMT2,MHSAIIP,PUMET,RNMT1
- 100ug (NPP3809) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11224-H09B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | DMNT2,DNMT2,MHSAIIP,PUMET,RNMT1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human TRDMT1/GST chimera consists of 616 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 71 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 60 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 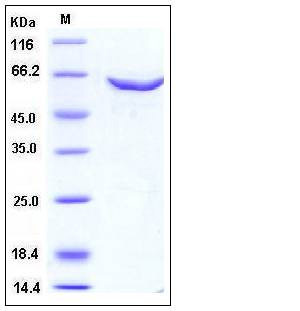 |
| Purity | > 94 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human TRDMT1 isoform a (NP_004403.1) (Met 1-Glu 391) was fused with the GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Epigenetics |DNA methylation |DNA methyltransferase |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, 0.5mM GSH, 0.5mM PMSF, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | DNMT2, also known as tRNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase, DNA methyltransferase homolog HsaIIP, and TRDMT1, is a member of the DNA methyltransferase family of enzymes. DNMT2 enzymes have been widely conserved during evolution and contain all of the signature motifs of DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferases. It contains all 10 sequence motifs that are conserved among m(5)C MTases, including the consensus S:-adenosyl-L-methionine-binding motifs and the active site ProCys dipeptide, and its structure is very similar to prokaryotic DNA methyltransferases. DNMT2 has close homologs in plants, insects and Schizosaccharomyces pombe, but no related sequence can be found in the genomes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae or Caenorhabditis elegans. While the biological function of DNMT2 is not yet known, the strong binding to DNA suggests that DNMT2 may mark specific sequences in the genome by binding to DNA through the specific target-recognizing motif. However, the DNA methyltransferase activity of these proteins is comparatively weak and their biochemical and functional properties remain enigmatic. Recent evidence now shows that Dnmt2 has a novel tRNA methyltransferase activity, raising the possibility that the biological roles of these proteins might be broader than previously thought. |
| Reference |
