Human DOPA Decarboxylase / DDC Protein (His Tag)
AADC
- 100ug (NPP2083) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10560-H08B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | AADC |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human DDC consists of 490 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 55 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 48 kDa protein in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 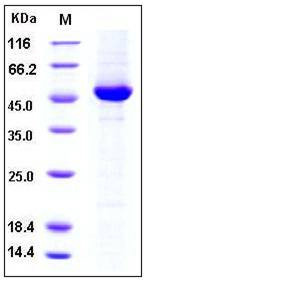 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the full length of human DDC (NP_000781.1) (Met 1-Glu 480) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to convert the substrate 3, 4-dihydroxy L-phenylalanine (L-Dopa) to 3, 4-dihydroxyphenylethylamine (dopamine). The dopamine product is measured by its absorbance at 340 nm after derivatization with trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid . The specific activity is >1500 pmoles/min/μg . |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Metabolism |Lipid metabolism |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, pH 8, 10% glycerol 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Dopa Decarboxylase (DDC), also known as AADC and Aromatic-L-amino acid decarboxylase, is a 54 kDa member of the group II decarboxylase family of proteins.It is a vitamin B6-dependent homodimeric enzyme that catalyzes the decarboxylation of both L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA) and L-5-hydroxytryptophan to dopamine and serotonin, respectively, which are major mammalian neurotransmitters and hormones belonging to catecholamines and indoleamines. Since L-DOPA is regularly used to treat the symptoms of Parkinson's disease, the catalytic pathway is of particular research interest. Defects of DDC are associated with severe developmental delay, oculogyric crises (OGC), as well as autosomal recessive disorder AADC deficiency, an early onset inborn error in neurotransmitter metabolism which can lead to catecholamine and serotonin deficiency. |
| Reference |
