Human DR6 / TNFRSF21 Protein
BM-018,CD358,DR6
- 100ug (NPP4324) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10175-HCCH |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | BM-018,CD358,DR6 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human DR6 consists of 315 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 34.2 kDa. By SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhDR6 is approximately 55-60 kDa due to the glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gln 42 |
| SDS-PAGE | 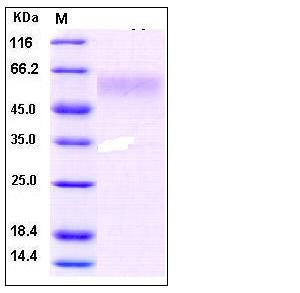 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | The mature form of human DR6 (NP_055267.1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Leu 350) with five amino acids (DDDDK) at the C-terminus was expressed and purified. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Other Related Intracellular Topics |Cellular Senescence and Pathways in Aging |Apoptosis |Apoptosis Receptors | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 100mM NaCl, 50mM Tris, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | TNFRSF21 (death receptor-6, DR6) is an orphan TNF receptor superfamily member and belongs to a subgroup of receptors called death receptors. This type I transmembrane receptor possesses four extracellular cysteine-rich motifs and a cytoplasmic death domain. DR6 is an extensively posttranslationally modified transmembrane protein and that N- and O-glycosylations of amino acids in its extracellular part. DR6 interacts with the adaptor protein TRADD and mediates signal transduction through its death domain, and expression of DR6 in mammalian cells induces activation of both NF-kappaB and JNK and cell apoptosis. DR6 knockout mice have enhanced CD4+ T cell proliferation and Th2 cytokine production, suggested that DR6 serves as an important regulatory molecule in T-helper cell activation, and is involved in inflammation and immune regulation. DR6 is expressed ubiquitously with high expression in lymphoid organs, heart, brain and pancreas. Some tumor cells overexpress DR6, typically in conjunction with elevated anti-apoptosis molecules. DR6 may also be involved in tumor cell survival and immune evasion, which is subject to future investigations. |
| Reference |
