Human DSC2 / Desmocollin-2 Protein (His Tag)
ARVD11,CDHF2,DG2,DGII/III,DSC3
- 100ug (NPP2087) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10809-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | ARVD11,CDHF2,DG2,DGII/III,DSC3 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human DSC2 (pro form) consists of 668 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 75 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rhDSC2 is approximately 85 and 100 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, corresponding to the mature and pro form respectively. |
| predicted N | Ala 28 & Arg 136 |
| SDS-PAGE | 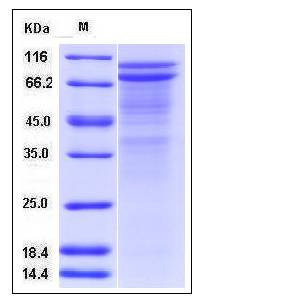 |
| Purity | > 75 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain (Met 1-Arg 684) of human DSC2 (Q02487-1) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Embryogenesis |Germ Layer Formation |Ectoderm Marker |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | DSC2 is a calcium-dependent glycoprotein that is a member of the desmocollin subfamily of the cadherin superfamily. Like other desmocollins, murine DSC2 has two products, Dsc2a and Dsc2b, produced by alternative splicing of a 46 bp exon which encodes 11 COOH-terminal aa followed by an in-frame stop codon. These desmosomal family members, along with the desmogleins, are found primarily in epithelial cells where they constitute the adhesive proteins of the desmosome cell-cell junction and are required for cell adhesion and desmosome formation. The desmosomal family members are arranged in two clusters on chromosome 18, occupying less than 650 kb combined. Mutations in DSC2 are associated with arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia-11. DSC2 is Involved in the interaction of plaque proteins and intermediate filaments mediating cell-cell adhesion. DSC2 may contribute to epidermal cell positioning by mediating differential adhesiveness between cells that express different isoforms. |
| Reference |
