Human DUSP14 / MKP-6 Protein (His & MBP Tag)
MKP-L,MKP6
- 100ug (NPP2088) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12443-H10E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | MKP-L,MKP6 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human DUSP14/MBP fusion protein consists of 587 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 65 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 60 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 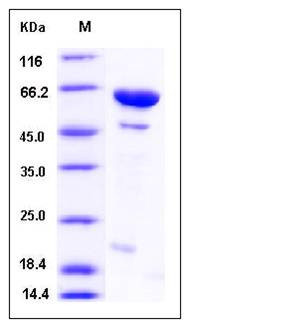 |
| Purity | > 88 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human DUSP14 (O95147) (Met 1 –His 191) was fused with an N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged MBP tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Protein Phosphorylation |Tyrosine Phosphatase |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Dual specific phosphatase 14 / MAP-kinase phophatase-6 (DUSP14 / MKP6) is a member of Dual-specificity phosphatases that is a subclass of protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTP) families that can dephosphorylate bothe phosphotyrosine and phosphoserine / phosphothreonine residues in substrates. Unlike many other DUSPs, DUSP14 only contains a catalytic domain within the C-terminal region. In signal transduction, DUSP14 has been considered as negative regulator of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) / extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 / 2 (ERK 1 / 2) pathway. DUSP14 phosphatase activity has been confirmed to be inhibited by PTP inhibitor Ⅳ. PTP inhibitor binds to the catalytic site of DUSP14. PTP inhibitor Ⅳ effectively and specifically inhibited DUSP14-mediated dephosphorylation of JNK, a member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family through dephosphorylation of both the Ser / Thr and Tyr residues of MAPKs. |
| Reference |
