Human Dim2 / TXNL4B Protein (His Tag)
Dim2,DLP
- 100ug (NPP3803) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13501-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | Dim2,DLP |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human TXNL4B consisting of 165 amino acids and migrates as an approximately 19 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions as predicted. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 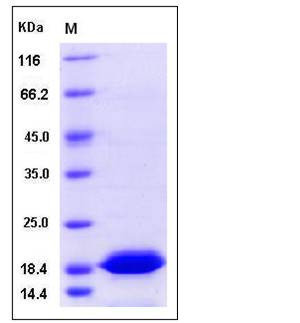 |
| Purity | > 92 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human TXNL4B (Q9NX01) (Met 1-Ile 149) was expressed, with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Epigenetics |DNA / RNA |RNA Processing |RNA splicing |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, 20% glycerol, 0.1% Tween20, 50mM Arg, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Dim2, also known as TXNL4B, is a member of the DIM1 family. The Dim protein family is composed of two classes, Dim1and Dim2, which share a common thioredoxin-like fold. They were originally identified for their role in cell cycle progression and have been found to interact with Prp6, an essential component of the spliceosome, which forms the bridge of U4/U6.U5-tri-snRNP. In spite of their biological and structural similarities, Dim1 and Dim2 proteins differ in many aspects. Dim1 bears distinctive structural motifs responsible for its interaction with other spliceosome components. Dim2 forms homodimers and contains specific domains required for its interactions with partners. This originality suggests that although both proteins are involved in pre-mRNA splicing, they are likely to be involved in different biological pathways. Dim2 roduced in E.Coli is a single, non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 185 amino acids and having a molecular mass of 21.1kDa. It is fused to a 36 amino acid His-tag at N-terminus & purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques. Dim2 has a vital role in pro-mRNA splicing. Dim2 is required in cell cycle progression for S/G2 transition and interacts with PRPF6 subunit of the spliceosome. |
| Reference |
