Human EBP1 / PA2G4 Protein (His Tag)
EBP1,HG4-1,p38-2G4
- 100ug (NPP2090) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12994-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | EBP1,HG4-1,p38-2G4 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human PA2G4 consisting of 404 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 45.2 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 32 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met 1 |
| SDS-PAGE | 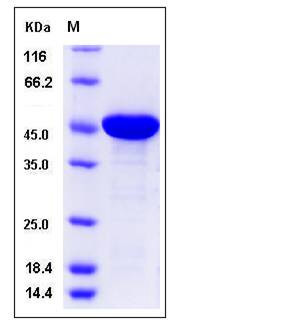 |
| Purity | > 92 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human PA2G4 (Q9UQ80) (Ser 2-Asp 394) was expressed, with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Epigenetics |Transcription |Other factors |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 0.5M NaCl, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | EBP1, also known as PA2G4, is an RNA-binding protein which belongs to the peptidase M24 family. It can be detected n several cell lines tested, including primary and transformed cell lines. EBP1 also present in pre-ribosomal ribonucleoprotein complexes and may be involved in ribosome assembly and the regulation of intermediate and late steps of rRNA processing. This protein is a transcriptional co-repressor of androgen receptor-regulated genes and other cell cycle regulatory genes through its interactions with histone deacetylases. PA2G4 can interact with the cytoplasmic domain of the ErbB3 receptor and may contribute to transducing growth regulatory signals. EBP1 has been implicated in growth inhibition and the induction of differentiation of human cancer cells. It seems to be involved in growth regulation. EBP1 also mediates cap-independent translation of specific viral IRESs (internal ribosomal entry site). |
| Reference |
