Human EF1B / EEF1B2 Protein (His Tag)
EEF1B,EEF1B1,EF1B
- 100ug (NPP2100) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P14611-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | EEF1B,EEF1B1,EF1B |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human EEF1B2 consists of 240 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 26.6 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 30 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 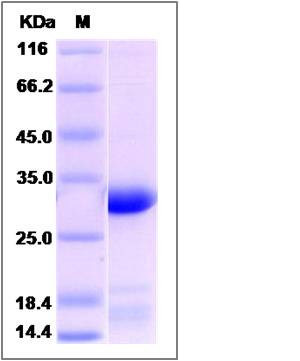 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human EEF1B2 (P24534)(Met1-Ile225) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Epigenetics |DNA / RNA |Translation |Ribosome |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, 10% Glycerol, 1mM DTT, pH 8.0. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | EF1B, also known as EEF1B2, is a translation elongation factor. It belongs to the EF-1-beta/EF-1-delta family. Elongation factors are a set of proteins that are used in protein synthesis in the cell. In the ribosome, they facilitate translational elongation, from the formation of the first peptide bond to the formation of the last one. EF1B is more complex in eukaryotes than in bacteria, and consists of three subunits: EF1B-alpha, EF1B-gamma and EF1B-beta. EF1B contains 1 GST C-terminal domain. It is involved in the transfer of aminoacylated tRNAs to the ribosome. EF1B is required to regenerate EF1A from its inactive form (EF1A-GDP) to its active form (EF1A-GTP). EF1A is then ready to interact with a new aminoacyl-tRNA to begin the cycle again. |
| Reference |
