Human EG-VEGF / prokineticin-1 Protein (His Tag)
EGVEGF,PK1,PRK1
- 100ug (NPP1580) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10183-H08B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | EGVEGF,PK1,PRK1 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human EG-VEGF consists of 96 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 11 KDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 15 Kda in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Ala 20 |
| SDS-PAGE | 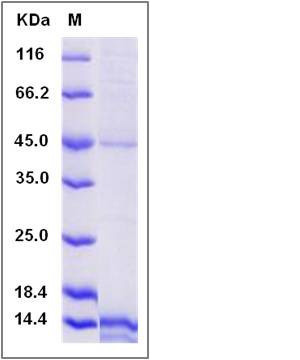 |
| Purity | > 89 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human EG-VEGF (Met 1-Phe105) (P58294) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Oncoprotein & suppressor & biomarker |Oncoprotein |Growth Factor & Receptor |Other Growth Factors & Receptors |Other Growth Factors | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 7.4, 0.02% Tween-80, 10% gly, 1mM DTT 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | EG-VEGF, also known as prokineticin-1, is a member of the AVIT (prokineticin) family. Prokineticins are secreted proteins that can promote angiogenesis and induce strong gastrointestinal smooth muscle contraction. EG-VEGF can be detected in the steroidogenic glands, ovary, testis, adrenal and placenta. EG-VEGF has little or no effect on a variety of other endothelial and non-endothelial cell types. It induces proliferation, migration and fenestration (the formation of membrane discontinuities) in capillary endothelial cells derived from endocrine glands. It directly influences neuroblastoma progression by promoting the proliferation and migration of neuroblastoma cells. EG-VEGF may play a role in placentation. It may also function in normal and pathological testis angiogenesis. It positively regulates PTGS2 expression and prostaglandin synthesis. |
| Reference |
