Human EGFL6 / EGF-L6 Protein (His Tag)
MAEG,W80
- 100ug (NPP1241) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10867-H08B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | MAEG,W80 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human EGFL6 consists of 542 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 60.5 KDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 62 KDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Asn 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 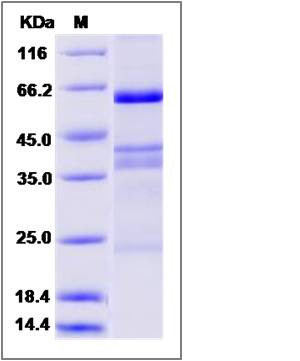 |
| Purity | > 60 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human EGFL6 (NP_056322.2)(Met1-Asp553) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the adhesion of NIH-3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cells. When 5 × 10E4 cells/well areadded to EGFL6-His coated plates (1.25μg/mL and 100μL/well),approximately 50-70% will adhere specifically after 30 minutes at 37℃. |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Metabolism |Types of disease |Metabolism in Obesity |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | EGFL6, also known as EGF-L6, belongs to the epidermal growth factor (EGF) repeat superfamily. Members of this superfamily are characterized by the presence of EGF-like repeats and are often involved in the regulation of cell cycle, proliferation, and developmental processes. EGFL6 contains a signal peptide, suggesting that it is secreted; an EGF repeat region consisting of 4 complete EGF-like repeats and 1 partial EGF-like repeat, 3 of which have a calcium-binding consensus sequence; an arg-gly-asp integrin association motif; and a MAM domain, which is believed to have an adhesive function. EGFL6 gene is expressed early during development, and its expression has been detected in lung and meningioma tumors. |
| Reference |
