Human EIF-5A / EIF5 Protein (GST Tag)
EIF-5,EIF-5A
- 100ug (NPP2101) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13932-H09E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | EIF-5,EIF-5A |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human EIF5 /GST chimera consists of 384 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 44.1 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 38-43 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 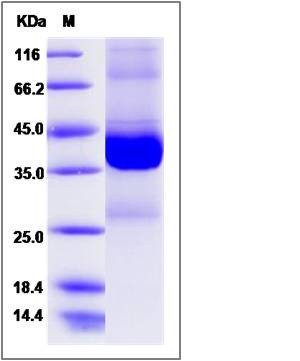 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human EIF5 (P55010) (Met1-Asp150) was fused with the GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Cytoskeleton / ECM |Cell Adhesion |Integrin |Beta integrin | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | EIF-5A, also known as EIF5, functions in start site selection as a GTPase accelerating protein (GAP) for the eukaryotic translation initiation factor (eIF) 2•GTP•tRNA ternary complex within the ribosome-bound pre-initiation complex. In protein synthesis initiation, eIF2 functions in its GTP-bound state to deliver initiator methionyl-tRNA to the small ribosomal subunit and is necessary for protein synthesis in all cells. EIF-5A stabilizes the binding of GDP to eIF2 and is therefore a bi-functional protein that acts as a GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI). EIF-5A also interacts with eIF1 and eIF3 and binds the eIF2-GTP/Met-tRNA ternary complex along with the 40S ribosome subunit. |
| Reference |
