Human ENO3 / beta-enolase Protein (His Tag)
ENO3
- 100ug (NPP2106) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P14270-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | ENO3 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human ENO3 consists of 449 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 48.8 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 45 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 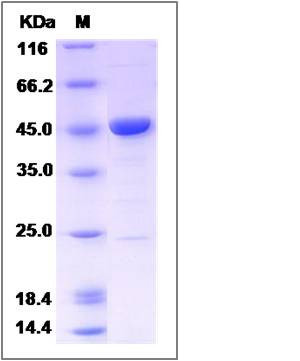 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human ENO3 (AAH17249.1) (Met1-Lys434) was expressed with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Metabolic signaling pathways |Carbohydrate metabolism |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 0.1% Brij35, pH 8.0. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | ENO3 is one of the three enolase isoenzymes found in mammals. As a homodimer, ENO3 is found in skeletal muscle cells in the adult. A switch from alpha enolase to beta enolase occurs in muscle tissue during development in rodents. Mutations in ENO3 gene can be associated with metabolic myopathies that may result from decreased stability of the enzyme. Two transcripts have been identified for ENO3 gene that differ only in their 5' UTR. ENO3 may play a role in muscle development and regeneration. It appears to have a function in striated muscle development and regeneration. |
| Reference |
