Human ESAM / Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule Protein (Fc Tag)
W117m
- 100ug (NPP2119) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10187-H02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | W117m |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human ESAM/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimeric protein. The reduced monomer consists of 457 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 50.5 kDa. By SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rh ESAM/Fc monomer is approximately 65-70 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gln 30 |
| SDS-PAGE | 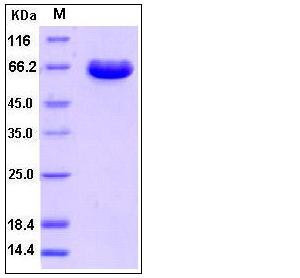 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain (Met 1-Ala 248) of human ESAM (NP_620411.2) precursor was expressed with the fused Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Invasion microenvironment |Adhesion molecule |Cell adhesion |Cell Adhesion Molecules |Endothelial | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 100mM Glycine, 10mM NaCl, 50mM Tris, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Endothelial cell-selective adhesion molecule (ESAM) is a member of JAM family of immunoglobulin superfamily and consists of one V-type and one C2-type immunoglobulin domain, as well as a hydrophobic signal sequence, a single transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic domain. It is specifically expressed at endothelial tight junctions and on activated platelets. ESAM at endothelial tight junctions participates in the migration of neutrophils through the vessel wall, possibly by influencing endothelial cell contacts. The adaptor protein membrane-associated guanylate kinase MAGI-1 has been identified as an intracellular binding partner of ESAM. Previous studies have indicated that ESAM regulates angiogenesis in the primary tumor growth and endothelial permeability. It suggest that ESAM has a redundant functional role in physiological angiogenesis but serves a unique and essential role in pathological angiogenic processes such as tumor growth. |
| Reference |
