Human EphA3 Protein (His Tag)
EK4,ETK,ETK1,HEK,HEK4,TYRO4
- 100ug (NPP1251) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11459-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | EK4,ETK,ETK1,HEK,HEK4,TYRO4 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human EPHA3 consists of 532 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 60.3 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 65-70 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Glu 21 |
| SDS-PAGE | 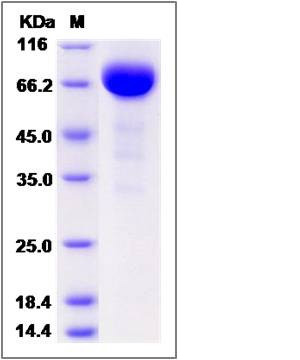 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human EPHA3 (Met1-Gln541) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized human EPHA3-His at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind human EphrinA5-Fc (P10192-H02H), The EC50 of human EphrinA5-Fc (P10192-H02H) is 6.2-14.6 ng/ml. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Invasion microenvironment |Angiogenesis |Eph Receptors |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | EPHA3 gene belongs to the ephrin receptor subfamily of the protein-tyrosine kinase family. EPH and EPH-related receptors have been implicated in mediating developmental events, particularly in the nervous system. The ephrin receptors are divided into 2 groups based on the similarity of their extracellular domain sequences and their affinities for binding ephrin-A and ephrin-B ligands. EPHA3 gene encodes a protein that binds ephrin-A ligands. EPHA3 is involved in the retinotectal mapping of neurons. It may also control the segregation but not the guidance of motor and sensory axons during neuromuscular circuit development. |
| Reference |
