Human EphB4 / HTK Protein (aa 563-987, His & GST Tag)
HTK,MYK1,TYRO11
- 100ug (NPP1254) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10235-H20B1 |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | HTK,MYK1,TYRO11 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human EPHB4/GST chimera consists of 662 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 75.2 kDa. The recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 66 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 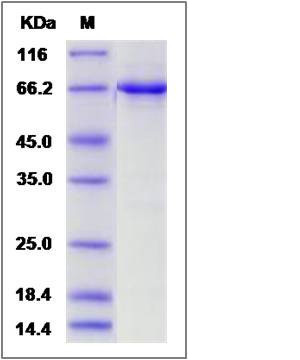 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human EPHB4 (P54760) (Leu563-Tyr987) was fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | The specific activity was determined to be 47 nmol/min/mg using Poly(Glu:Tyr) 4:1 as substrate. |
| Research Area | Epigenetics |Transcription |Cancer susceptibility |Tumor Suppressor |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 8.0, 3mM DTT, 10% gly 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Ephrin type-B receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EPHB4 gene. It is a single-pass type I membrane protein belonging to the ephrin receptor subfamily of protein kinase superfamily. Members of the ephrin and Eph family are local mediators of cell function through largely contact-dependent processes in development and in maturity. Furthermore, EphB4 protein and the corresponding ligand Ephrin-B2 contribute to tumor growth in various human tumors. EphB4 protein has tumor suppressor activities and that regulation of cell proliferation, extracellular matrix remodeling, and invasive potential are important mechanisms of tumor suppression. Therefore, Ephrin-B2/EphB4 may be recognized as a novel prognostic indicator for cancers. |
| Reference |
