Human EphB6 / EphB6 Protein
HEP
- 100ug (NPP3842) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10197-HCCH |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | HEP |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mature human EphB6 consists of 569 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 60.4 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhEphB6 is approximately 72 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Leu 17 |
| SDS-PAGE | 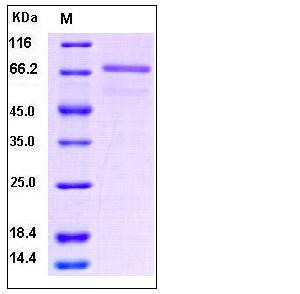 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE and SEC-HPLC Analysis. |
| Protein Construction | The mature form of human EphB6 (NP_004436.1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Ser 579) with quinary-aa peptide (DDDDK) at the C-terminus was expressed and purified. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized human EphB6 (P10197-HCCH) at 10 μg/mL (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated human EFNB2-Fch (P10881-H03H) with a linear range of 1.56-50 ng/mL. |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Growth Factor & Receptor |Ephrin & Eph Receptor |Eph Receptor |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 100mM NaCl, 50mM Tris, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Ephrins are divided into the ephrin-A (EFNA) class and the ephrin-B (EFNB) class based on their structures and sequence relationships. Ephrin receptors make up the largest subgroup of the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family. EphB6 is an unusual Eph receptor, lacking catalytic capacity due to alterations in its kinase domain. Interestingly, increased metastatic activity is associated with reduced EphB6 receptor expression in several tumor types, including breast cancer. This emphasizes the potential of EphB6 to act as a suppressor of cancer aggressiveness. EphB6 suppress cancer invasiveness through c-Cbl-dependent signaling, morphologic changes, and cell attachment and indicate that EphB6 may represent a useful prognostic marker and a promising target for therapeutic approaches. EphB6 can both positively and negatively regulate cell adhesion and migration, and suggest that tyrosine phosphorylation of the receptor by an Src family kinase acts as the molecular switch for the functional transition. In addition, Ephrin-B2 may be a physiological ligand for the EphB6 receptor. |
| Reference |
