Human Ephrin-A3 / EFNA3 Protein (His Tag)
EFL2,Ehk1-L,EPLG3,LERK3
- 100ug (NPP1255) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10188-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | EFL2,Ehk1-L,EPLG3,LERK3 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human EphrinA3 consists of 202 amino acids after removal of the signal peptide and has a predicted molecular mass of 23 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhEphrinA3 is approximately 35-40 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gln 23 |
| SDS-PAGE | 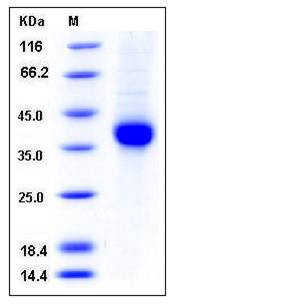 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human EphrinA3 (NP_004943.1) (Met 1-Ser 213) with the C-terminal propeptide removed was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to compete with human EphrinA3 / Fc for binding to immobilized mouse EphA6-his in a functional ELISA assay. |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Neurology process |Growth and Development |Axon Guidance |Ephrin & Eph Receptor |Ephrin | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Ephrin-A3 also known as EPH-related receptor tyrosine kinase ligand 3 or EFNA3, is a member of the ephrin family. The Eph family receptor interacting proteins (ephrins) are a family of proteins that serve as the ligands of the Eph receptor, which compose the largest known subfamily of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases (RTKs). Ephrin-A3 and their Eph family of receptor tyrosine kinases are expressed by cells of the SVZ. Ephrin subclasses are further distinguished by their mode of attachment to the plasma membrane: Ephrin-A3 ligands bind EphA receptors and are anchored to the plasma membrane via a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) linkage, whereas ephrin-B ligands bind EphB receptors and are anchored via a transmembrane domain. Ephrin-A3 expressed on astrocytes activates EphA4 on the post-synaptic neuron and restricts the growth of dendritic spines through multiple pathways. |
| Reference |
