Human FES Kinase / Feline sarcoma oncogene Protein (His & GST Tag)
FPS
- 100ug (NPP3858) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12214-H20B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | FPS |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human FES/GST chimera consists of 1060 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 121 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 110 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 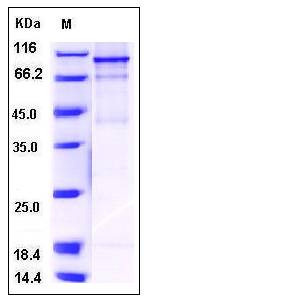 |
| Purity | > 75 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human FES (P07332-1) (Met 1-Arg 822) was fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | The specific activity was determined to be 200 nmol/min/mg using Poly(Glu:Tyr) 4:1 as substrate. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Akt Pathway |Intracellular Kinases in the Akt Pathway |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 7.4, 10% glycerol 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Fes/Fps, also known as Proto-oncogene c-Fes, Proto-oncogene c-Fps, Feline sarcoma oncogene, FES and FPS, is a protein which contains one FCH domain, one protein kinase domain and one SH2 domain. FES is a non-receptor protein tyrosine kinase expressed in hematopoietic progenitors and differentiated myeloid cells. FES is observed in the nuclear, granular and plasma membrane fractions of primary human neutrophils and the myeloid leukemia cell line, HL-60. The nuclear localization is confirmed by immunocytochemistry of neutrophils. FES has been implicated in granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), interleukin-3 (IL-3) and erythropoietin signal transduction. FES has tyrosine-specific protein kinase activity and that activity is required for maintenance of cellular transformation. FES is also involved in normal hematopoiesis. Its chromosomal location has linked it to a specific translocation event identified in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia. |
| Reference |
