Human FGF17 Protein
FGF-13,FGF-17,HH20
- 100ug (NPP1277) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12342-HNAE |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | FGF-13,FGF-17,HH20 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human FGF17 consists of 195 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 22.6 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 21 and 23 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 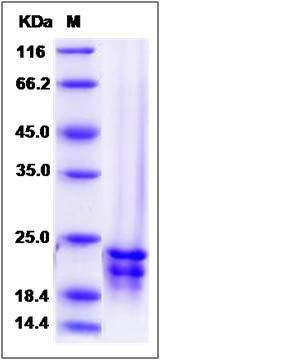 |
| Purity | (39.1+60.0) % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human FGF17 (O60258-1) (Thr23-Thr216) was expressed, with a N-terminal Met. |
| Bio-activity | Measured in a cell proliferation assay using BALB/c 3T3 mouse fibroblasts. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.6-3 μg/mL. |
| Research Area | Cardiovascular |Angiogenesis |Growth Factor & Receptor |Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) & Receptor |Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 1M NaCl, PH 8.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | FGF-13, also known as FGF17, belongs to the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. Members of this family show broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and play a role in a variety of biological processes including embryonic development cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. FGF-13 is preferentially expressed in the embryonic brain. It interacts with FGFR3 and FGFR4. FGF-13 plays an important role in the regulation of embryonic development and as signaling molecule in the induction and patterning of the embryonic brain. It is also required for normal brain development. |
| Reference |
