Human FGF21 Protein (His Tag)
UNQ3115 / PRO10196
- 100ug (NPP1281) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10911-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | UNQ3115 / PRO10196 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human FGF21 consisting of 188 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 20.2 kDa. It migrates as an 23 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions as predicted. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 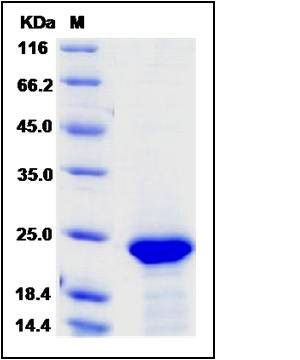 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human FGF21 (NP_061986.1) (His 29-Ser 209) was expressed, with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Morphogenesis |Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) & Receptor |Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 50 mM Tris, 10 % glycerol, 0.05 % Brig 35, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities and are involved in a variety of biological processes including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. FGF-21 has a hydrophobic amino terminus, which is a typical signal sequence, and appears to be a secreted protein. The metabolic regulator fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) has antidiabetic properties in animal models of diabetes and obesity. FGF21 is a novel adipokine associated with obesity-related metabolic complications in humans. The paradoxical increase of serum FGF21 in obese individuals, which may be explained by a compensatory response or resistance to FGF21, warrants further investigation. FGF-21, which we have identified as a novel metabolic factor, exhibits the therapeutic characteristics necessary for an effective treatment of diabetes. |
| Reference |
