Human FGFR3 / CD333 Protein (alpha(IIIb), Fc Tag)
ACH,CD333,CEK2,HSFGFR3EX,JTK4
- 100ug (NPP3944) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P16486-H02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | ACH,CD333,CEK2,HSFGFR3EX,JTK4 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human FGFR3(alpha(IIIb)) consists 593 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 65.3 kDa. |
| predicted N | Glu 23 |
| SDS-PAGE | 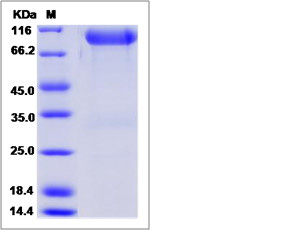 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human FGFR3(alpha(IIIb)) (NP_001156685.1) (Met1-Gly377) was expressed with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Cluster of Differentiation (CD) |Other CD Antigen |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | FGFR3, also known as CD333, is a member of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) family, with its amino acid sequence being highly conserved between members and among divergent species. FGFR family members differ from one another in their ligand affinities and tissue distribution. FGFRs are transmembrane catalytic receptors that have intracellular tyrosine kinase activity. Mutations in FGFR genes are the cause of several human developmental disorders characterized by skeletal abnormalities such as achondroplasia, and upregulation of FGFR expression may lead to cell transformation and cancer. FGFR3, a full-length representative protein would consist of an extracellular region, composed of three immunoglobulin-like domains, a single hydrophobic membrane-spanning segment and a cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase domain. The extracellular portion of FGFR3 interacts with fibroblast growth factors, setting in motion a cascade of downstream signals, ultimately influencing mitogenesis and differentiation. FGFR3 binds acidic and basic fibroblast growth hormone and plays a role in bone development and maintenance. Mutations in FGFR3 gene lead to craniosynostosis and multiple types of skeletal dysplasia. Three alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different protein isoforms have been described. CD333 is the receptor for acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. |
| Reference |
