Human FLRT1 Protein (His Tag)
SPG68
- 100ug (NPP3868) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11389-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | SPG68 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human FLRT1 consists of 515 amino acids and predictes a molecular mass of 57 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rh FLRT1 is approximately 65 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Ile 21 |
| SDS-PAGE | 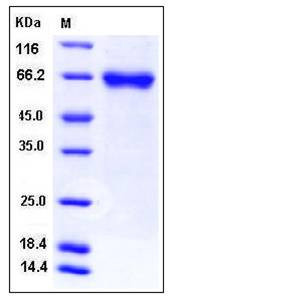 |
| Purity | > 96 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human FLRT1 extracellular domain (Q9NZU1-1) (Met 1-Pro 524) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the adhesion of Neuro‑2A mouse neuroblastoma cells. When cells are added to coated plates(5μg/mL, 100μL/well), approximately 50%-70% will adhere after 1 hour at 37℃. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Innate Immunity |Monocytes/Macrophages |Monocyte Markers |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The three fibronectin leucine-rich repeat transmembrane (FLRT) proteins contain 10 leucine-rich repeats (LRR), a type III fibronectin (FN) domain, followed by the transmembrane region, and a short cytoplasmic tail. FLRT1 is expressed in kidney and brain, which is a target for tyrosine phosphorylation mediated by FGFR1 and implicate a non-receptor Src family kinase (SFK). All FLRTs can interact with FGFR1 and FLRTs can be induced by the activation of FGF signalling by FGF-2. The phosphorylation state of FLRT1, which is itself FGFR1 dependent, may play a critical role in the potentiation of FGFR1 signalling and may also depend on a SFK-dependent phosphorylation mechanism acting via the FGFR. This is consistent with an 'in vivo' role for FLRT1 regulation of FGF signalling via SFKs. Furthermore, the phosphorylation-dependent futile cycle mechanism controlling FGFR1 signalling is concurrently crucial for regulation of FLRT1-mediated neurite outgrowth. FLRT1, FLRT2 and FLRT3 are members of the fibronectin leucine rich transmembrane protein (FLRT) family. They may function in cell adhesion and/or receptor signalling. Their protein structures resemble small leucine-rich proteoglycans found in the extracellular matrix. FLRT3 shares 55% amino acid sequence identity with FLRT1. |
| Reference |
