Human FUT8 Protein (aa 68-575, His Tag)
MGC26465
- 100ug (NPP2141) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11326-H08B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | MGC26465 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human FUT8 consists of 518 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 60 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 55 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Arg 68 |
| SDS-PAGE | 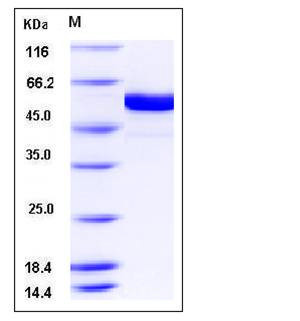 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human FUT8 isoform 1 (Q9BYC5-1) (Arg 68-Lys 575) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the carboxy-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to hydrolyze the donor substrate GDP fucose. The specific activity is >0.75 pmoles/min/μg. |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Metabolism |Types of disease |Metabolism in Cancer |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 8.0, 10% gly 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Human alpha (1,6) fucosyltransferase 8, also known as FUT8, is a member of the glycosyltransferase family. Fucosyltransferases are the enzymes transferring fucose from GDP-Fuc to Gal in an alpha1,2-linkage and to GlcNAc in alpha1,3-linkage, alpha1,4-linkage, or alpha1,6-linkage. All fucosyltransferases utilize the same nucleotide sugar, their specificity reside in the recognition of the acceptor and in the type of linkage formed. Fucosyltransferases share some common structural and catalytic features. On the basis of protein sequence similarities, these enzymes can be classified into four distinct families: (1) the alpha-2-fucosyltransferases, (2) the alpha-3-fucosyltransferases, (3) the mammalian alpha-6-fucosyltransferases, and (4) the bacterial alpha-6-fucosyltransferases. The alpha-3-fucosyltransferases constitute a distinct family as they lack the consensus peptide, but some regions display similarities with the alpha-2 and alpha-6-fucosyltranferases. |
| Reference |
