Human G-CSF / CSF3 Protein (isoform b)
C17orf33,C17orf33OS,CSF3OS,G-CSF,GCSF
- 100ug (NPP3881) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10007-HNCE |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | C17orf33,C17orf33OS,CSF3OS,G-CSF,GCSF |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human GCSFb consists of 175 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 18.7 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 18 kDa protein in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Ala 30 |
| SDS-PAGE | 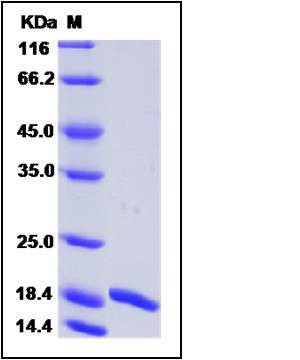 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human GCSF isoform b (NP_757373.1) (Ala30-Pro204) was expressed. |
| Bio-activity | Measured in a cell proliferation assay using NFS-60 mouse myelogenous leukemia lymphoblast cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.04-0.2 ng/mL. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Invasion microenvironment |Angiogenesis |Angiogenesis Growth Factor & Receptor |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) is a growth factor and an essential cytokine belonging to the CSF family of hormone-like glycoproteins. It is produced by numerous cell types including immune and endothelial cells. G-CSF binding to its receptor G-CSF-R which belongs to the cytokine receptor type I family depends on the interaction of alpha-helical motifs of the former and two fibronectin type III as well as an immunoglobulin-like domain of the latter. Recent animal studies have also revealed that G-CSF activates multiple signaling pathways, such as Akt and also the Janus family kinase-2 and signal transducer and activation of transcription-3 (Jak2-STAT3) pathway, thereby promoting survival, proliferation, differentiation and mobilisation of haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. G-CSF is a cytokine that have been demonstrated to improve cardiac function and perfusion in myocardial infarction. And it was initially evaluated as a stem cell mobilizer and erythropoietin as a cytoprotective agent. G-CSF prevents left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction by decreasing cardiomyocyte death and by increasing the number of blood vessels, suggesting the importance of direct actions of G-CSF on the myocardium rather than through mobilization and differentiation of stem cells. Accordingly, recombinant human (rh)G-CSF has been extensively used in clinical haematology and oncology to enable bone marrow transplantation or to treat chemotherapy-associated neutropenia. In preclinical study, G-CSF improved cardiac function and perfusion by angiomyogenesis and protection of cardiomyocytes in myocardial infarction. |
| Reference |
