Human G-CSFR / CD114 / CSF3R Protein
CD114,G-CSF R,GCSFR
- 100ug (NPP2143) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10218-HCCH |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD114,G-CSF R,GCSFR |
| Molecular Weight | The mature recombinant human G-CSFR consists of 63 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 69.0 KDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rhG-CSFR is approximately 94 KDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Glu 25 |
| SDS-PAGE | 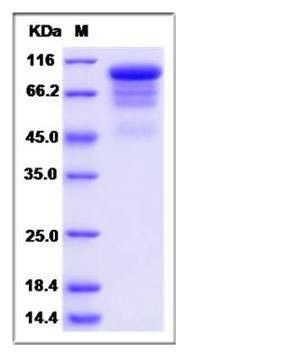 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | The mature form of human G-CSF receptor (NP_000751.1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Pro 621) with five aminio acids at the C-terminus was expressed and purified. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to inhibit GCSF-induced proliferation of NFS60 mouse myeloid cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 2-8 μg/mL. |
| Research Area | Cardiovascular |Angiogenesis |Growth Factor & Receptor |Colony-Stimulating Factor (CSF) & Receptor |CSF Receptor |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor Receptor (G-CSFR), also known as CD114, which belongs to the cytokine receptor superfamily, is a cell surface receptor for colony stimulating factor 3 (CSF3). It is a critical regulator of granulopoiesis. This type I membrane protein has a composite structure consisting of an immunoglobulin(Ig)-like domain, a cytokine receptor-homologous (CRH) domain and three fibronectin type III (FNIII) domains in the extracellular region. Mutations in the G-CSF receptor leading to carboxy-terminal truncation transduce hyperproliferative growth responses, and are implicated in the pathological progression of severe congenital neutropenia (SCN) to acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). Additionally, autocrine/paracrine stimulation of G-CSFR may be important in the biology of solid tumors, including metastasis. |
| Reference |
