Human GALE / UDP galactose-4-epimerase Protein (His Tag)
SDR1E1
- 100ug (NPP2146) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P14810-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | SDR1E1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human GALE consists of 363 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 40.1 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 36 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 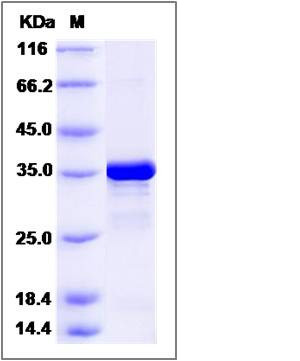 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human GALE (Q14376) (Met1-Ala348) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM HEPES, 150mM NaCl, 10% Glycerol, pH 7.5. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | UDP galactose-4'-epimerase, also known as GALE, enables the body to process a simple sugar called galactose, which is present in small amounts in many foods. Galactose is primarily part of a larger sugar called lactose, which is found in all dairy products and many baby formulas. UDP galactose-4'-epimerase catalyzes two distinct but analogous reactions: the epimerization of UDP-glucose to UDP-galactose, and the epimerization of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine to UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine. Defects in GALE causes epimerase-deficiency galactosemia (EDG), also known as galactosemia type 3. Clinical features include early-onset cataracts, liver damage, deafness and mental retardation. |
| Reference |
