Human GALK1 / Galactokinase / Galactose kinase Protein (His & GST Tag)
GALK,GK1,HEL-S-19
- 100ug (NPP2149) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11383-H20B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | GALK,GK1,HEL-S-19 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human GALK1/GST chimera consists of 629 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 70 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 60 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 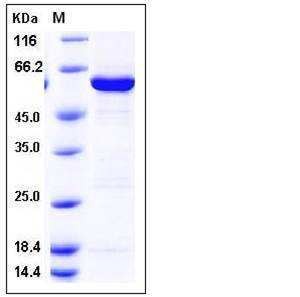 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human GALK1 (P51570) (Met 1-Leu 392) was fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Kinase activity untested |
| Research Area | Cancer |Cancer Metabolism |Metabolic signaling |Metabolism of carbohydrate |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 2mM GSH, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Galactokinase, also known as Galactose kinase, GALK and GALK1, is a protein which belongs to the GHMP kinase family and GalK subfamily. Galactokinase / GALK1 is a major enzyme for galactose metabolism. Galactokinase (GALK) deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by elevation of blood galactose concentration and diminished galactose-1-phosphate, leading to the production of galactitol. Defects in GALK1 are the cause of galactosemia II ( GALCT2 ) which II is an autosomal recessive deficiency characterized by congenital cataracts during infancy and presenile cataracts in the adult population. The cataracts are secondary to accumulation of galactitol in the lenses. |
| Reference |
