Human GCAP1 / GUCA1A Protein (His & GST Tag)
C6orf131,COD3,CORD14,dJ139D8.6,GCAP,GCAP1,GUCA,GUCA1
- 100ug (NPP3913) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P14565-H20B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | C6orf131,COD3,CORD14,dJ139D8.6,GCAP,GCAP1,GUCA,GUCA1 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human GUCA1A consists of 438 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 50.7 KDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 42 KDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 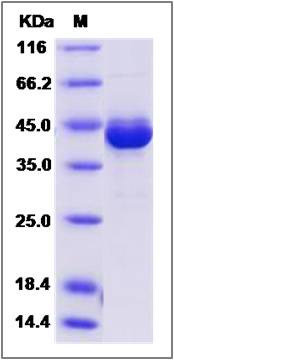 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human GUCA1A (P43080)( Met1-Gly201) was expressed the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Signaling Pathway |Calcium Signaling |Calcium Binding Proteins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | GCAP 1 gene plays a role in the recovery of retinal photoreceptors from photobleaching. In the recovery phase, the phototransduction messeneger cGMP is replenished by retinal guanylyl cyclase-1 (GC1). GC1 is activated by decreasing Ca(2+) concentrations following photobleaching. The protein encoded by this gene, guanylyl cyclase activating protein 1 (GCAP 1), mediates the sensitivity of GC1 to Ca(2+) concentrations. GCAP 1 promotes activity of GC1 at low Ca(2+) concentrations and inhibits GC1 activity at high Ca(2+) concentrations. Mutations in GCAP 1 gene cause autosomal dominant cone dystrophy (COD3); a disease characterized by reduced visual acuity associated with progressive loss of color vision. GCAP 1 stimulates guanylyl cyclase 1 (GC1) when free calcium ions concentration is low and inhibits GC1 when free calcium ions concentration is elevated. This Ca(2+)-sensitive regulation of GC is a key event in recovery of the dark state of rod photoreceptors following light exposure. |
| Reference |
