Human GFRA1 / GFRα1 / GDNFRA Protein (His Tag)
GDNFR,GDNFRA,GFR-ALPHA-1,RET1L,RETL1,TRNR1
- 100ug (NPP3889) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10330-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | GDNFR,GDNFRA,GFR-ALPHA-1,RET1L,RETL1,TRNR1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human GFRα1 consists of 411 amino acids after removal of the signal peptide and predicts a molecular mass of 46 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the rhGFRα1 migrates as an approximately 55-60 kDa protein in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Asp 25 |
| SDS-PAGE | 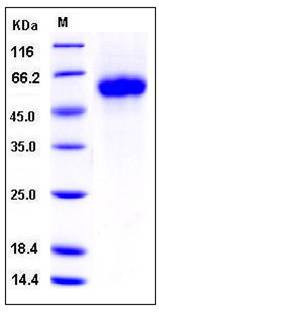 |
| Purity | > 98 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human GFRα1 without the propeptide (NP_665736.1) (Met 1-Ser 424) was fused with the a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured in a cell proliferation assay using SH‑SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.2-1 μg/mL in the presence of 40 ng/mL Recombinant Human GDNF. 2. Measured by its ability to bind human GDNF (native) in functional ELISA. |
| Research Area | Cardiovascular |Angiogenesis |Cytokine & Receptor |Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGF-beta) Superfamily |TGF-beta Superfamily Receptors |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) Family Receptor Alpha 1 (GFRA1) is a member of the GDNF receptor family. It is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked cell surface receptor for both GDNF and NTN, and mediates activation of the RET tyrosine kinase receptor. GFRA1 is a potent survival factor for central and peripheral neurons, and is essential for the development of kidneys and the enteric nervous system. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) and neurturin (NTN) are its binding ligand which are two structurally related, potent neurotrophic factors that play key roles in the control of neuron survival and differentiation. GDNF promotes the formation of a physical complex between GFRA/GDNFRa and the orphan tyrosin kinase receptor Ret, thereby inducing its tyrosine phosphorylation. The RET is a receptor tyrosine kinase representing the signal-transducing molecule of a multisubunit surface receptor complex for the GDNF, in which GFRA / GDNFRa acts as the ligand-binding component. GDNF, a distantly related member of the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-â) superfamily, and its receptor components: GFRA1, Ret and neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) have been recently reported to be expressed in the testis and to be involved in the proliferation regulation of immature Sertoli cells. |
| Reference |
