Human GM2A Protein (His Tag)
GM2-AP,SAP-3
- 100ug (NPP2164) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13246-H08B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | GM2-AP,SAP-3 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human GM2A (pro form) comprises 180 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 19.8 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of rh GM2A is approximately 25 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Val 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 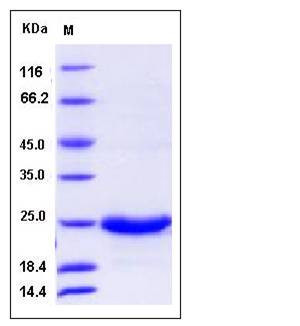 |
| Purity | > 96 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human GM2A (AAA35907.1) (Met 1-Ile 193) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Metabolism |Types of disease |Metabolism in Cancer |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 7.4, 10% gly 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | GM2A (GM2 ganglioside activator), is a lipid transfer protein which belongs to the ML domain family. GM2A can accommodate several single chain phospholipids and fatty acids. It also exhibits some calcium-independent phospholipase activity. GM2A binds gangliosides and stimulates ganglioside GM2 degradation. It stimulates only the breakdown of ganglioside GM2 and glycolipid GA2 by beta-hexosaminidase A. GM2A acts as a substrate specific co-factor for the lysosomal enzyme β-hexosaminidase A. β-hexosaminidase A, together with GM2 ganglioside activator, catalyzes the degradation of the ganglioside GM2, and other molecules containing terminal N-acetyl hexosamines. It extracts single GM2 molecules from membranes and presents them in soluble form to beta-hexosaminidase A for cleavage of N-acetyl-D-galactosamine and conversion to GM3. Defects in GM2A are the cause of GM2-gangliosidosis type AB (GM2GAB), also known as Tay-Sachs disease AB variant. |
| Reference |
