Human GNGT1 / GNG1 Protein (His Tag)
GNG1
- 100ug (NPP2167) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13658-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | GNG1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human GNGT1 consisting of 85 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 9.9KDa. It migrates as a 9.0 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions as predicted. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 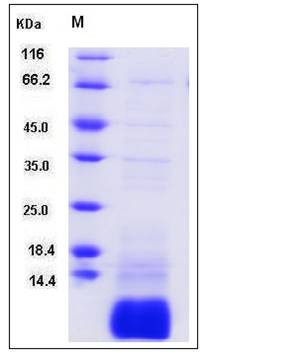 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature foem of human GNGT1 (P63211) (Pro 2-Cys 71) was expressed, with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | GNGT1 is a subunit of of transducin. Heterotrimeric G proteins consist of alpha, beta, and gamma subunits. They are membrane bound GTPases that are linked to 7-TM receptors. They function as signal transducers for the 7-transmembrane-helix G protein-coupled receptors. They are involved as a modulator or transducer in various transmembrane signaling systems. G proteins are bound to GDP in the 'off' state. GNGT1 is the gamma subunit of transducin. Ligand-receptor binding results in detachment of the G protein, switching it to an 'on' state and permitting Galpha activation of second messenger signalling cascades. There are several types of Galpha proteins; in addition, some Gbetagamma subunits have active functions. Gbetagamma coupled to H1 receptors can activate PLA2 and Gbetagamma coupled to M1 receptors can activate KIR channels. The beta and gamma chains are required for the GTPase activity, for replacement of GDP by GTP, and for G protein-effector interaction. |
| Reference |
