Human GRK2 / ADRBK1 Protein (His & GST Tag)
BARK1,BETA-ARK1,GRK2
- 100ug (NPP3909) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11755-H20B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | BARK1,BETA-ARK1,GRK2 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human ADRBK1/GST chimera consists of 926 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 107 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 110 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 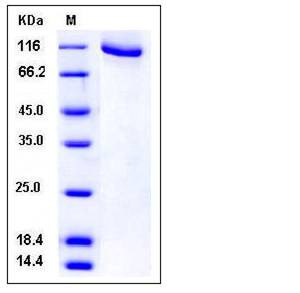 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human ADRBK1 (NP_001610.2) (Met 1-Leu 689) was fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | No Kinase Activity |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Signaling Pathway |G Protein Signaling |Heterotrimeric G Proteins |GPCR Kinases | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 0.5mM GSH, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | G-protein coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2), also referred as Adrenergic, beta, receptor kinase 1 (ADRBK1), is a ubiquitous member of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK) family that appears to play a central, integrative role in signal transduction cascades. GRK2 can phosphorylate a growing number of non-GPCR substrates and associate with a variety of proteins related to signal transduction, thus suggesting that this kinase could also have diverse 'effector' functions. GRK2 has been reported to interact with a variety of signal transduction proteins related to cell migration such as MEK, Akt, PI3Kgamma or GIT. Interestingly, the levels of expression and activity of this kinase are altered in a number of inflammatory disorders (as rheumatoid arthritis or multiple sclerosis), thus suggesting that GRK2 may play an important role in the onset or development of these pathologies. The important physiological function of GRK2 as a modulator of the efficacy of GPCR signal transduction systems is exemplified by its relevance in cardiovascular physiopathology as well as by its emerging role in the regulation of chemokine receptors. Besides its canonical role in the modulation of the signalling mediated by many G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR), this protein can display a very complex network of functional interactions with a variety of signal transduction partners, in a stimulus, cell type, or context-specific way. |
| Reference |
