Human GSTZ1 Protein (His Tag)
GSTZ1,GSTZ1-1,MAAI,MAI
- 100ug (NPP2174) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P14237-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | GSTZ1,GSTZ1-1,MAAI,MAI |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human GSTZ1 consists of 231 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 26 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 27 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 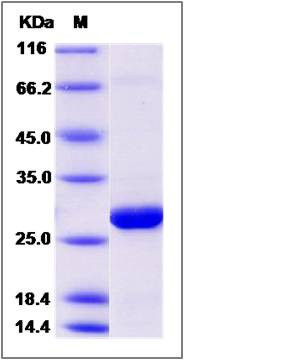 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human GSTZ1 (NP_665877.1) (Met1-Ala216) was expressed with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Metabolism |Amino Acids |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, 10% glycerol, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | GSTZ1 gene is a member of the glutathione S-transferase (GSTs) super-family which encodes multifunctional enzymes important in the detoxification of electrophilic molecules, including carcinogens, mutagens, and several therapeutic drugs, by conjugation with glutathione. GSTZ1 is a bifunctional protein which has minimal glutathione-conjugating activity with ethacrynic acid and 7-chloro-4-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazole and maleylacetoacetate isomerase activity. GSTZ1 catalyzes the glutathione dependent oxygenation of dichloroacetic acid to glyoxylic acid. GSTZ1 participates in the catabolism of phenylalanine and tyrosine. Thus defects in GSTZ1 cause harsh metabolic disorders including alkaptonuria, phenylketonuria and tyrosinaemia. |
| Reference |
