Human Glutaredoxin / GRX1 / GLRX Protein (His Tag)
GLRX,GRX,GRX1
- 100ug (NPP2163) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P14484-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | GLRX,GRX,GRX1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human GLRX consists of 121 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 13.6 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 12 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 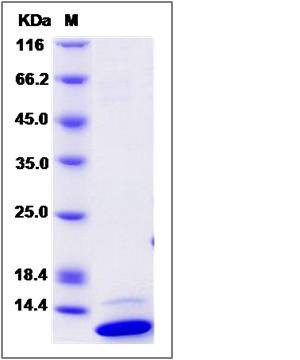 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human GLRX (P35754)(Met1-Gln106) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Redox metabolism |Oxidative stress | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tirs, 10% Glycerol, 1mM DTT, pH 8.0. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Glutaredoxin-1, also known as GRX1 and GLRX, belongs to the glutaredoxin family. Glutaredoxins are small redox enzymes that use glutathione as a cofactor. Glutaredoxins are oxidized by substrates, and reduced non-enzymatically by glutathione. Glutaredoxin-1 functions as an electron carrier in the glutathione-dependent synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides by the enzyme ribonucleotide reductase. Glutaredoxin-1 exists in either a reduced or an oxidized form. Glutaredoxins function as electron carriers in the glutathione-dependent synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides by the enzymeribonucleotide reductase. |
| Reference |
