Human Glypican 5 / GPC5 Protein (His Tag)
GPC5, bA93M14.1, glypican proteoglycan 5, glypican-5
- 100ug (NPP3896) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10079-H08B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | GPC5, bA93M14.1, glypican proteoglycan 5, glypican-5 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human GPC5 consists of 540 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 60.5 kDa as estimated in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Glu 25 |
| SDS-PAGE | 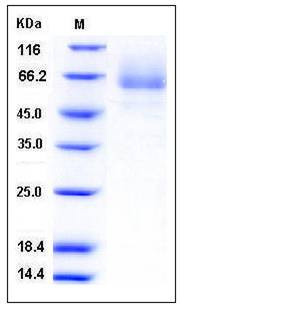 |
| Purity | > 92 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human GPC5 (NP_004457.1) (Met 1-Thr 554) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA . Immobilized human GPC5 at 5 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind human bFGF with a linear ranger of 0.156-2.5 ng/ml . |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Cytoskeleton / ECM |HSPGs |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Glypican-5 (GPC5), is a cell membrane protein which belongs to the glypican family. The glypicans compose a family of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored heparan sulfate proteoglycans that may play a role in the control of cell division and growth regulation. So far, six members (Glypican-1/GPC1, Glypican-2/GPC2, Glypican-3/GPC3, Glypican-4/GPC4, Glypican-5/GPC5, Glypican-6/GPC6) of this family are known in vertebrates. In adult, Glypican-5 is primarily expressed in the brain. It is also detected in fetal brain, lung and liver. Glypican-5 enhances the intracellular signaling of FGF2 and HGF. It alters the cellular distribution of FGF2. The properties of Glypican-5 make it an attractive target for therapeutic intervention in rhabdomyosarcomas and other tumors that amplify and/or overexpress its gene. Glypican-5 is over-expressed in lymphoma cell lines that had shown amplification. It is a likely target for amplification, and that over-expression of GPC5 may contribute to development and/or progression of lymphomas and other tumors. |
| Reference |
