Human Granzyme B / GZMB Protein (His Tag)
CCPI,CGL-1,CGL1,CSP-B,CSPB,CTLA1,CTSGL1,HLP,SECT
- 100ug (NPP2171) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10345-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CCPI,CGL-1,CGL1,CSP-B,CSPB,CTLA1,CTSGL1,HLP,SECT |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human Granzyme B consists of 240 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 27 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rhGranzyme B is approximately 36 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gly 19 |
| SDS-PAGE | 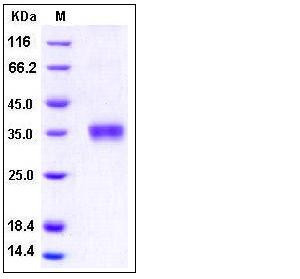 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the proform of human Granzyme B (NP_004122.1) (Met 1-Tyr 247) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Other Related Intracellular Topics |Cellular Senescence and Pathways in Aging |Apoptosis |Extracellular Signals | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Granzyme B, also known as GZMB, is the most prominent member of the granzyme family of cell death-inducing serine proteases expressed in the granules of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and NK cells. Granzyme B enters the target cells depending on another membrane-binding granule protein, perforin, results in the activation of effector caspases and mitochondrial depolarization through caspase-dependent and -independent pathways, and consequently induces rapid cell apoptosis. Over 30 substrates of GZMB have been identified including the key substrate caspase-3, ICAD and Bid. GZMB is suggested to protect the host by lysing cells bearing on their surface 'nonself' antigens such as bacterial and viral infected-cells and tumor cells, and accordingly plays an essential role in immunosurveillance. |
| Reference |
