Human Granzyme H Protein (His Tag)
CCP-X,CGL-2,CSP-C,CTLA1,CTSGL2,GZMH
- 100ug (NPP3908) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10348-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CCP-X,CGL-2,CSP-C,CTLA1,CTSGL2,GZMH |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human Granzyme H comprises 239 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 26.7 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, rh Granzyme H migrates as an approximately 36 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Glu 19 |
| SDS-PAGE | 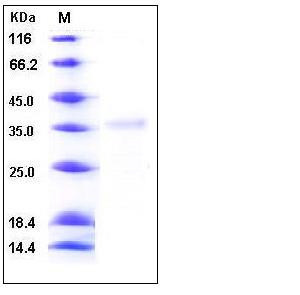 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human Granzyme H (NP_219491.1) (Met 1-Leu 246) with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag was expressed. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Cellular Senescence and Pathways in Aging |Apoptosis |Extracellular Signals |Granzyme | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Granzymes are key components of the immune response that play important roles in eliminating host cells infected by intracellular pathogens. Several granzymes are potent inducers of cell death. A total of eight granzymes (A-G and M) have been identified in the mouse, but only five are known in humans (A, B, H, M and granzyme 3), and granzyme H appears to be specifically human. Human granzyme H is a neutral serine protease that is expressed predominantly in the lymphokine-activated killer (LAK)/natural?killer (NK) compartment of the immune system. In adenovirus-infected cells in which granzyme B (gzmB) and downstream apoptosis pathways are inhibited, granzyme H directly cleaves the adenovirus DNA-binding protein (DBP), a viral component absolutely required for viral DNA replication. This virus demonstrated that gzmH directly induces an important decay in viral DNA replication. Interestingly, gzmH also cleaves the adenovirus 100K assembly protein, a major inhibitor of gzmB, and relieves gzmB inhibition. Granzyme H has a very high amino acid identity (>90%) with many portions of the granzyme B sequence, particularly near the amino terminus of the molecule despite performing a distinct enzymic function. |
| Reference |
