Human HIF-1 alpha / HIF1A Protein (His Tag)
bHLHe78,HIF-1A,HIF-1alpha,HIF1,HIF1-ALPHA,MOP1,PASD8
- 100ug (NPP3920) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11977-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | bHLHe78,HIF-1A,HIF-1alpha,HIF1,HIF1-ALPHA,MOP1,PASD8 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human HIF1A consisting of 259 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 28.4 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 34 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 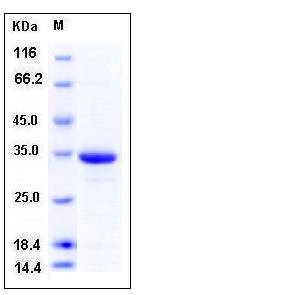 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human HIF1A isoform 1 (Q16665-1) N-terminal segment (Arg 575-Asn 826) was expressed, with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Transcription Factors and Regulators |HIF Transcription Factors |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | HIF-1 alpha, also known as HIF1A, contains 1 basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) domain, 1 PAC (PAS-associated C-terminal) domain and 2 PAS (PER-ARNT-SIM) domains. It is one of the two subunits of Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF1). HIF1 is a transcription factor found in mammalian cells cultured under reduced oxygen tension that plays an essential role in cellular and systemic homeostatic responses to hypoxia. HIF1 is a heterodimer composed of an alpha subunit and a beta subunit. The beta subunit has been identified as the aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT). HIF-1 alpha is expressed in most tissues with highest levels in kidney and heart. It is overexpressed in the majority of common human cancers and their metastases, due to the presence of intratumoral hypoxia and as a result of mutations in genes encoding oncoproteins and tumor suppressors. HIF-1 alpha functions as a master transcriptional regulator of the adaptive response to hypoxia. Under hypoxic conditions, it activates the transcription of over 40 genes, including erythropoietin, glucose transporters, glycolytic enzymes, vascular endothelial growth factor, HILPDA, and other genes whose protein products increase oxygen delivery or facilitate metabolic adaptation to hypoxia. HIF1A plays an essential role in embryonic vascularization, tumor angiogenesis and pathophysiology of ischemic disease. HIF-1 alpha binds to core DNA sequence 5'-[AG]CGTG-3' within the hypoxia response element (HRE) of target gene promoters. Activation requires recruitment of transcriptional coactivators such as CREBPB and EP300. |
| Reference |
