Human HIST3H2A / Histone H2A Protein
MGC3165
- 100ug (NPP3921) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10926-HNAE |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | MGC3165 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human HIST3H2A consists of 130 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 14.2 kDa as estimated in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met 1 |
| SDS-PAGE | 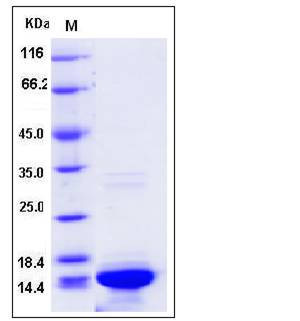 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human HIST3H2A (NP_254280.1) (Met 1-Lys 130) was expressed and purified. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Epigenetics |Histone |H2A |Variants |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM β-Mercaptoethanol, pH 6.9 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Histones are a complex family of highly conserved basic proteins responsible for packaging chromosomal DNA into nucleosomes. There are subtype diversities: H1, H2A, H2B and H3 or H4. It has become more and more evident that histone modifications are key players in the regulation of chromatin states and dynamics as well as in gene expression. Therefore, histone modifications and the enzymatic machineries that set them are crucial regulators that can control cellular proliferation, differentiation, plasticity, and malignancy processes. However, extracellular histones are a double-edged sword because they also damage host tissue and may cause death. Histones bound to platelets, induced calcium influx, and recruited plasma adhesion proteins such as fibrinogen to induce platelet aggregation. Histone cluster 3, H2a also known as histone H2A (HIST3H2A) is a member of histones. Covalent modification of histones is important in regulating chromatin dynamics and transcription. One example of such modification is ubiquitination, which mainly occurs on histones H2A and H2B. E3 ubiquitin ligase complex is specific for histone H2A (HIST3H2A). Reducing the expression of Ring2 results in a dramatic decrease in the level of ubiquitinated H2A in HeLa cells. DNA damage induces monoubiquitylation of histone H2A (HIST3H2A) in the vicinity of DNA lesions. |
| Reference |
