Human HOXA1 Protein (His Tag)
BSAS,HOX1,HOX1F
- 100ug (NPP3925) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12644-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | BSAS,HOX1,HOX1F |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human HOXA1 consisting of 346 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 38 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 42 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 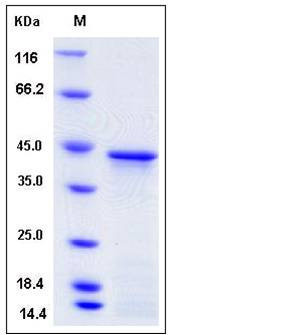 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human HOXA1 isoform 3 (P49639-1) (Met 1-His 335) was expressed, with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Transcription Factors and Regulators |Homeodomain (Hox) Transcription Factors |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 30% glycerol, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Homeobox protein Hox-A1 is a transcription factor encoded by HOXA1 gene. This gene is one of the four types of homeobox genes each of which contains a homobox DNA sequence that codes for the homeodomain, a region of 60 amino acids responsible for the DNA binding exhibited by these homeobox proteins. These Homeobox genes are essential metazoan genes as they determine the identity of embryonic regions along the anterio-posterior axis. The homeobox protein Hox-A1 may be involved in the placement of hindbrain segments in the proper location along the anterior-posterior axis during development. Early in its development, the vertebrate hindbrain is transiently subdivided into a series of compartments called rhombomeres. Genes have been identified whose expression patterns distinguish these cellular compartments. Two of these genes, Hoxa1 and Hoxa2, have been shown to be required for proper patterning of the early mouse hindbrain and the associated neural crest. It has been detected HOXA1 expression in a variety of human breast cancer lesions, suggesting that HOXA1 may be required for the establishment of breast cancer cells phenotype. |
| Reference |
