Human HSP70 / HSPA1A Protein (His Tag)
HEL-S-103,HSP70-1,HSP70-1A,HSP70I,HSP72,HSPA1
- 100ug (NPP3929) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11660-H07B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | HEL-S-103,HSP70-1,HSP70-1A,HSP70I,HSP72,HSPA1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human HSPA1A consists of 658 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 72.2 kDa. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 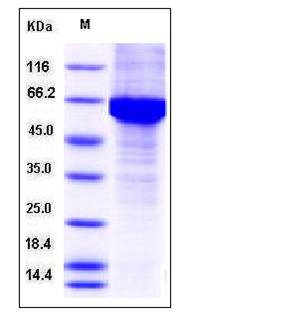 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human HSPA1A (NP_005337.2) (Ala2-Asp641) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its ability to bind human PARP1 in a functional ELISA. 2. Measured by its ability to bind mouse PARP1 in a functional ELISA. |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Other Related Intracellular Topics |Heat Shock Proteins (HSPs) |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 7.4, 10% gly 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | HSPA1A is a member of the Hsp70 protein family. The 70 kilodalton heat shock proteins (Hsp70s) are a family of ubiquitously expressed heat shock proteins. HSP are abundant and conserved proteins present in all cells. Upon temperature shock or other stress stimuli, HSP are synthesized intracellularly, which may protect cells from protein denaturation or from death. Extracellularly, HSP can serve a cytokine function to initiate both innate and adaptive immunity through activation of APC. HSP serves also a chaperone function and facilitates presentation of antigen peptide to T cells. Molecular chaperones of the Hsp70 family have diverse functions in cells. They assist the folding of newly synthesized and stress-denatured proteins, as well as the import of proteins into organelles, and the dissociation of aggregated proteins. The well-conserved Hsp70 chaperones are ATP dependent: binding and hydrolysis of ATP regulates their interactions with unfolded polypeptide substrates, and ATPase cycling is necessary for their function. All cellular functions of Hsp70 chaperones use the same mechanism of ATP-driven polypeptide binding and release. |
| Reference |
