Human Hemojuvelin / HFE2 Protein (His Tag)
HFE2A,HJV,JH,RGMC
- 100ug (NPP2180) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10410-H08B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | HFE2A,HJV,JH,RGMC |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human HFE2 consists of 374 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 40 kDa. As a result of intracellular cleavage, the apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 20, 34 and 44 KDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, corresponding to the N-terminal, C-terminal portions and the full-length respectively. |
| predicted N | Gln 36 |
| SDS-PAGE | 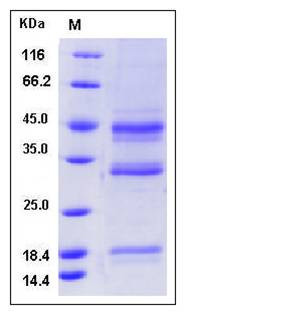 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human HFE2 isoform a (Q6ZVN8-1) (Met 1-Ser 399) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Vitamins / minerals |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, 500mM NaCl, pH 7.0, 10% gly 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Hemojuvelin, also known as HFE2, is a membrane-bound and soluble protein which belongs to the repulsive guidance molecule (RGM) family. It is known that RGMs function through Neogenin, a homologue of the Netrin receptor deleted in colon cancer. In mammals, RGM family consists of three glycoproteins which have discrete expression patterns and functions (RGM-A, RGM-B, and RGM-C). Hemojuvelin is expressed in adult and fetal liver, heart, and skeletal muscle. Hemojuvelin acts as a bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) coreceptor. Enhancement of BMP signaling regulates hepcidin (HAMP) expression and iron metabolism. It plays a key role in iron metabolism. Hemojuvelin represents the cellular receptor for hepcidin. It may be a component of the signaling pathway which activates hepcidin or it may act as a modulator of hepcidin expression. Defects in hemojuvelin are the cause of hemochromatosis type 2A, also known as juvenile hemochromatosis (JH). |
| Reference |
