Human I-TAC / CXCL11 Protein
b-R1,H174,I-TAC,IP-9,IP9,SCYB11,SCYB9B
- 100ug (NPP1558) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10876-HNAE |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | b-R1,H174,I-TAC,IP-9,IP9,SCYB11,SCYB9B |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CXCL11 consists of 73 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 8.3 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 9 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 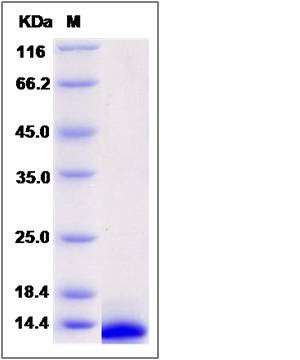 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human CXCL11 (O14625) (Phe22-Phe94) was expressed with an initial Met. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Neurology process |Neurodegeneration and Neurodegenerative Disease |Others in Neurodegeneration and Neurodegenerative Disease |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 40% acetonitrile, 1% TFA 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | I-TAC, also known as CXCL11, is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family. It is highly expressed in peripheral blood leukocytes, pancreas and liver, with moderate levels in thymus, spleen and lung and low expression levels were in small intestine, placenta and prostate. The I-TAC chemokine elicits its effects on its target cells by interacting with the cell surface chemokine receptor CXCR3, with a higher affinity than do the other ligands for this receptor, CXCL9 and CXCL10. I-TAC is chemotactic for activated T cells. The CXCL11 gene is located on human chromosome 4 along with many other members of the CXC chemokine family. |
| Reference |
