Human ICAM-1 / CD54 Protein (His Tag)
BB2,CD54,ICAM-1,P3.58
- 100ug (NPP3969) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10346-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | BB2,CD54,ICAM-1,P3.58 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human ICAM1 consists of 464 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 51 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rhICAM1 is approxiamtely 65-70 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gln 28 |
| SDS-PAGE | 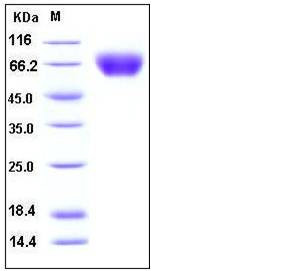 |
| Purity | > 98 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human ICAM1 (NP_000192.2) extracellular domain (Met 1-Glu 480) was fused with the a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the adhesion of PMA-stimulated HSB2 human peripheral blood acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. When cells are added to ICAM1-coated plates (12.5 μg/ml, 100 μl/well), approximately 30%-60% will adhere specifically. |
| Research Area | Microbiology |Pathogenic microorganism |viruses |animal virus |viral illness |Viral tract respiratory illness | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1, or CD54) is a 90 kDa member of the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily and is critical for the firm arrest and transmigration of leukocytes out of blood vessels and into tissues. ICAM-1 is constitutively present on endothelial cells, but its expression is increased by proinflammatory cytokines. The endothelial expression of ICAM-1 is increased in atherosclerotic and transplant-associated atherosclerotic tissue and in animal models of atherosclerosis. Additionally, ICAM-1 has been implicated in the progression of autoimmune diseases. ICAM-1 is a ligand for LFA-1(integrin). When activated, leukocytes bind to endothelial cells via ICAM-1/LFA-1 interaction and then transmigrate into tissues. Presence with heavy glycosylation and other structural characteristics, ICAM-1 possesses binding sites for a number of immune-associated ligands and serves as the binding site for entry of the major group of human Rhinovirus (HRV) into various cell types. ICAM-1 also becomes known for its affinity for Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes (PFIE), providing more of a role in infectious disease. Previous studies have shown that ICAM-1 is involved in inflammatory reactions and that a defect in ICAM-1 gene inhibits allergic contact hypersensitivity. |
| Reference |
