Human ICOS Ligand / B7-H2 / ICOSLG Protein (Fc Tag)
ICOSLG, B7H2, B7RP1, ICOSL, KIAA0653
- 100ug (NPP1560) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11559-H02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | ICOSLG, B7H2, B7RP1, ICOSL, KIAA0653 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human ICOSLG/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 481 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 53.7 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 66-76 and 33 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Asp 19 |
| SDS-PAGE | 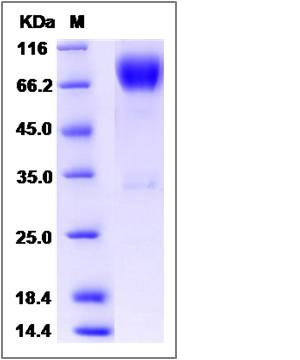 |
| Purity | (96.1+2.0) % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human ICOSLG (O75144-1) (Met1-Ser258) was expressed with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Adaptive Immunity |Costimulation & Costimulatory Molecule |B7/CD28 Family |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Inducible co-stimulator ligand (ICOSL), also known as B7-H2, is a member of the B7 family of co-stimulatory molecules related to B7-1 and B7-2. It is a transmembrane glycoprotein with extracellular IgV and IgC domains, and binds to ICOS on activated T cells, thus delivers a positive costimulatory signal for optimal T cell function. The structural features of ICOSL are crucial for its costimulatory function. Present study shows that ICOSL displays a marked oligomerization potential, resembling more like B7-1 than B7-2. B7-H2-dependent signaling may play an active role in a proliferative response rather than in cytokine and chemokine production. The CD28/B7 and ICOS/B7-H2 pathways are both critical for costimulating T cell immune responses. Deficiency in either pathway results in defective T cell activation, cytokine production and germinal center formation. |
| Reference |
