Human IDO1 / IDO Protein
IDO,IDO-1,INDO,Indoleamine 2,3‑dioxygenase
- 100ug (NPP3975) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11650-HNCE |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | IDO,IDO-1,INDO,Indoleamine 2,3‑dioxygenase |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human IDO1 consists of 403 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 45.2 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 46 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gly |
| SDS-PAGE | 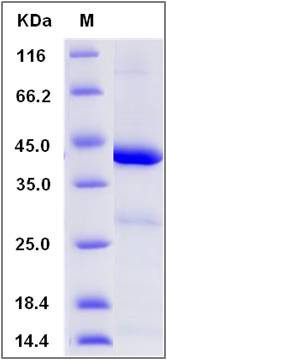 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human IDO1 (NP_002155.1) (Ala2-Gly403) was expressed and purified with one additional amino acids (Gly) at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to oxidize L-tryptophan to N-formylk-ynurenine. The specific activity is > 500 pmoles/min/μg. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Cell cycle |Oxidative Stress |Anti-oxidant Molecules |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 50 mM NaAC, 100 mM Nacl, 20 % glycerol, pH 5.5. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-1, also known as Indoleamine-pyrrole 2,3-dioxygenase, IDO1 and IDO, is a member of the indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase family. IDO1 / IDO and tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO) are tryptophan-degrading enzymes that catalyze the first step in tryptophan catabolism via the kynurenine pathway. TDO is widely distributed in both eukaryotes and bacteria. In contrast, IDO has been found only in mammals and yeast. In 2007, a third enzyme, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-2 (IDO2), was discovered. IDO2 is found not only in mammals but also in lower vertebrates. IDO1 / IDO is an immunosuppressive molecule inducible in various cells. IDO1 / IDO catalyzes the cleavage of the pyrrol ring of tryptophan and incorporates both atoms of a molecule of oxygen. It mediates oxidative cleavage of tryptophan, an amino acid essential for cell proliferation and survival. IDO1 / IDO inhibition is proposed to have therapeutic potential in immunodeficiency-associated abnormalities, including cancer. The IDO pathway is activated in multiple tumor types. Selective inhibition of IDO1 may represent an attractive cancer therapeutic strategy via up-regulation of cellular immunity. IDO1 / IDO is an enzyme that suppresses adaptive T-cell immunity by catabolizing tryptophan from the cellular microenvironment. Inhibition of IDO pathway might enhance the efficacy of immunotherapeutic strategies for cancer. |
| Reference |
