Human IFNAR2 / IFNABR Protein (Fc Tag)
IFN-alpha-REC,IFN-R,IFNABR,IFNARB
- 100ug (NPP3982) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10359-H02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | IFN-alpha-REC,IFN-R,IFNABR,IFNARB |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human IFNAR2/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimeric protein. The reduced monomer consists of 458 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 51.8 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rh IFNAR2/Fc monomer is approximately 65-75 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Ile 27 |
| SDS-PAGE | 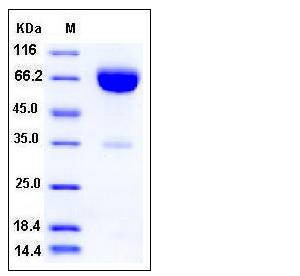 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of human IFNAR2 isoform a (NP_997468.1) (Met 1-Lys 243) was fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to inhibit rh IFNβ mediated protection of WISH Human amnion cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) to viral lysis. The EC50 for this effect is typically 0.01-0.05 μg/mL. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Invasion microenvironment |Angiogenesis |Cytokine & Receptor |Interferon & Receptor |Interferon receptor | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Interferon-alpha/beta receptor beta chain (IFNAR2) is a type I membrane protein that forms one of the two chains of a receptor for interferons alpha and beta. Binding and activation of the receptor stimulates Janus protein kinases, which in turn phosphorylate several proteins, including STAT1 and STAT2. Initial cell-surface IFNAR2 expression at diagnosis assessed by flow cytometry widely distributed but showed overall significantly higher expression in CML patients when compared with normal controls. In 15 fresh patients who subsequently received IFNα therapy, IFNAR2 expression at diagnosis was significantly higher in cytogenetic good responders than in poor responders. Down-regulation of IFNAR2 expression during IFNα therapy was observed only in good responders but not in poor responders. The encoded protein also functions as an antiviral factor. IFNAR2 may associate with IFNAR1 to form the type I interferon receptor. This protein serves as a receptor for interferons alpha and beta. IFNAR2 is also involved in IFN-mediated STAT1, STAT2 and STAT3 activation. Isoform 1 and isoform 2 are directly involved in signal transduction due to their association with the TYR kinase, JAK1. Isoform 3 is a potent inhibitor of type I IFN receptor activity. Following binding of IFNα2, IFNAR2 is internalized, but, instead of being routed towards degradation as it is when complexed to IFNβ, it recycles back to the cell surface. |
| Reference |
