Human IL-1R8 / IL1RAPL1 Protein (His Tag)
IL1R8,IL1RAPL,MRX10,MRX21,MRX34,OPHN4,TIGIRR-2
- 100ug (NPP2268) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10177-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | IL1R8,IL1RAPL,MRX10,MRX21,MRX34,OPHN4,TIGIRR-2 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human IL1R8 consists of 347 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 40 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rh IL1R8 is approximately 50-55 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Leu 19 |
| SDS-PAGE | 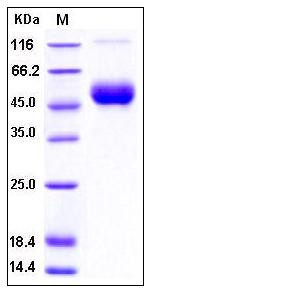 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human IL1R8 (NP_055086.1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Leu 354) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Neurotransmission |Calcium Signaling |Calcium Channel |N-type |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein-like 1 (IL1RAPL1) is a member of interleukin-1 receptor family. The protein structurally comprises three extracellular immunoglobulin domains, which presumably mediate binding of an as yet unidentified ligand, a transmembrane region, and an intracellular domain, which is likely to enable signalling via the NFkB pathway. The means of signalling is almost certain to be identical to that used by the IL1R family and the more distally related Toll protein. L1RAPL1 protein physically interacts via its 150 aa C-terminal domain with neuronal calcium sensor-1 (NCS-1), a protein widely expressed in neurons and the related chromaffin and PC12 cells. IL1RAPL1 is an integral membrane protein responsible for a nonsyndromic form of mental retardation (MR). It is suggested to affect human cognitive ability to some extent, especially the memory and concentration capability. |
| Reference |
